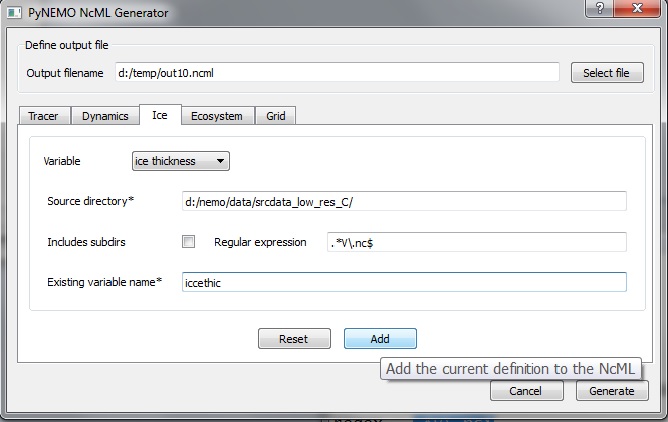
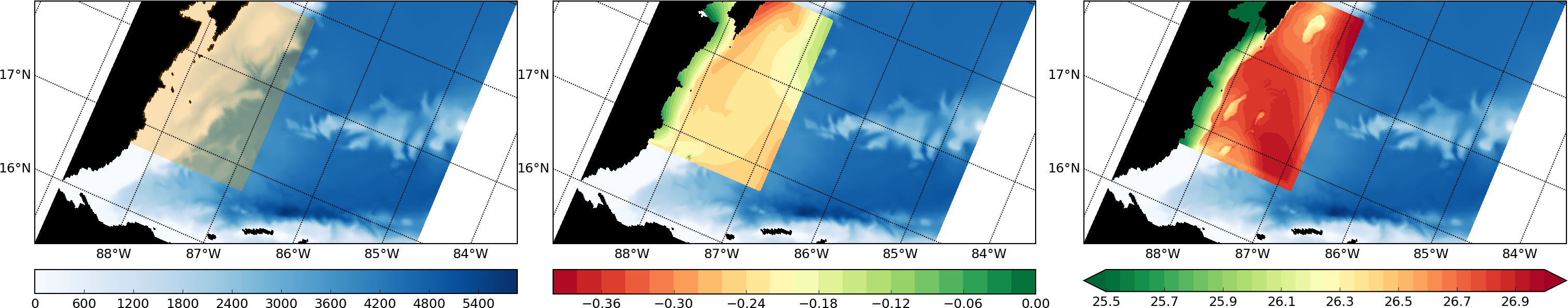
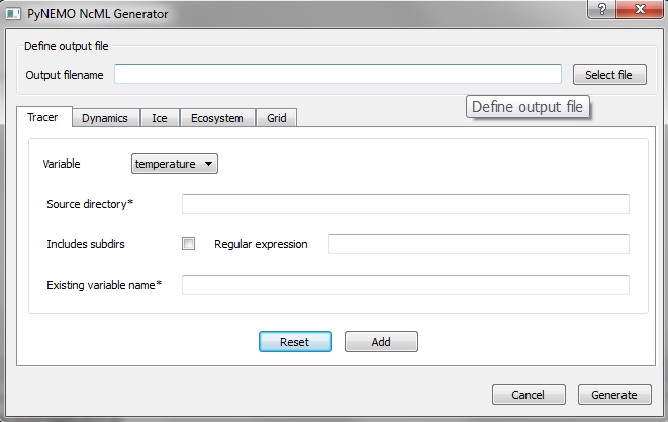
Add the beginnings of RST documentation
Showing
docs/Makefile
0 → 100644
docs/make.bat
0 → 100644
62.5 KB
docs/source/_static/eg2.png
0 → 100644
373 KB
52.5 KB
docs/source/conf.py
0 → 100644
docs/source/examples.rst
0 → 100644
docs/source/index.rst
0 → 100644
docs/source/installation.rst
0 → 100644
docs/source/intro.rst
0 → 100644
docs/source/usage.rst
0 → 100644